Female hair loss refers to the condition where women experience a noticeable reduction in hair volume or thickness. It can result from various factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, stress, or medical conditions.
Unraveling the mystery behind female hair loss involves exploring various factors. Ever wondered why some women experience hair loss? From hormonal changes to genetics, let’s delve into the reasons behind this common concern and discover what causes those strands to bid farewell.
Female hair loss can result from various factors. Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute. Medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders may also play a role. Nutritional deficiencies, especially in iron and vitamins, can impact hair health.
Symptoms Of Hair Loss In Women
Hair loss in women can manifest through various symptoms. Excessive shedding, thinning of hair, and widening part lines are common signs. Women may notice more hair in brushes or on shower floors. Hormonal changes, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and genetics often contribute.
- Excessive Shedding: Women experiencing hair loss often notice increased hair shedding during routine activities like brushing or showering, leading to concerns about the overall volume and thickness of their hair.
- Thinning Hair and Widening Part Lines: Symptomatic hair thinning and widening part lines are common signs of female hair loss, reflecting changes in hair density and distribution, prompting women to seek solutions for these visible shifts.
- Hormonal Imbalances and Hair Loss: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute to hair loss in women. Understanding the connection between hormonal changes and hair health is crucial for effective intervention and management.
- Identifying Underlying Causes: Recognizing that factors like stress, nutritional deficiencies, genetics, medications, and medical conditions can contribute to hair loss empowers women to address the root causes and seek appropriate interventions, emphasizing the importance of professional guidance.
Illnesses That Cause Hair Loss In Women
Hair loss in women can be attributed to various illnesses. Conditions such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and hormonal imbalances can lead to significant hair thinning or shedding. For example, hypothyroidism can disrupt the balance of hormones crucial for hair growth, resulting in noticeable loss.
- Thyroid Disorders: Understanding the Link to Hair Loss. Women experiencing hair loss should explore the connection with thyroid conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, as imbalances in thyroid hormones can disrupt the normal growth cycle of hair follicles, leading to noticeable thinning.
- Autoimmune Diseases and Alopecia Areata: Unveiling the Impact on Women’s Hair. Delve into the role of autoimmune disorders, specifically alopecia areata, where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. Recognizing these conditions is pivotal for addressing the root cause of hair loss in women.
- Hormonal Imbalances During Pregnancy and Menopause: Navigating the Changes Affecting Hair Health. Explore the intricate relationship between hormonal fluctuations during significant life stages like pregnancy and menopause and the subsequent impact on women’s hair.
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals: Key Steps in Diagnosing and Treating Hair Loss. Highlight the importance of seeking professional medical advice when facing hair loss issues. Healthcare professionals can conduct thorough assessments, identify underlying illnesses, and propose tailored treatments, ensuring effective management and potential reversal of hair loss in women.
Female Hair Loss Treated
Female hair loss can be effectively treated through various methods. Treatment options may include medications like minoxidil, which promotes hair growth, or hormonal therapies to address imbalances. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can contribute to hair health.
- Understanding the Causes: Explore the diverse reasons behind female hair loss, from hormonal imbalances to genetics. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective treatment.
- Medical Interventions: Discover the range of medical treatments available, including medications like minoxidil and hormonal therapies. A healthcare professional can guide you through personalized options for optimal results.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Factors: Explore how a healthy lifestyle and a nutrient-rich diet contribute to managing female hair loss. Simple changes in habits and nutrition can play a significant role in promoting hair health.
- Innovative Solutions: Investigate emerging solutions such as laser therapy and specialized shampoos tailored to address female hair loss. Stay informed about the latest developments in the field for comprehensive and effective treatment options.
Diet For Healthy Hair and Growth

Maintaining a diet for healthy hair and growth involves incorporating nutrient-rich foods to support strong and vibrant locks. Essential elements like vitamins A, C, and E, as well as biotin and omega-3 fatty acids, play pivotal roles in promoting hair health. Include fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in your daily meals to provide the necessary building blocks for hair growth.
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for promoting healthy hair and facilitating growth. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides essential vitamins and minerals that support hair health. Nutrients like biotin, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids contribute to strong, shiny hair and stimulate growth.
Menopause and hormone imbalances
Menopause, a natural phase in a woman’s life, marks the end of reproductive years. During this transition, hormonal fluctuations can lead to various symptoms. Estrogen and progesterone levels decline, causing hot flashes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances. Hormone imbalances can also affect bone health and increase the risk of cardiovascular issues.
While menopause is inevitable, its impact can be managed through lifestyle changes, a balanced diet, and, if necessary, hormone replacement therapy. Understanding these hormonal shifts empowers women to navigate this stage with greater resilience and seek medical guidance for personalized solutions to alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being.
Hair loss risk factors
Hair loss risk factors can be influenced by various elements, including genetics, hormonal changes, and medical conditions. Genetics plays a crucial role, as individuals with a family history of hair loss are more susceptible. Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause, can also contribute. Seeking appropriate treatments and adopting a healthy lifestyle helps address women’s hair loss concerns effectively.
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors significantly influence hair loss, with individuals having a family history more prone to this condition. Understanding your family’s hair health can provide insights into potential risks and preventive measures.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause, can contribute to hair loss. Awareness of these hormonal changes is crucial for early detection and intervention to minimize the risk.
- Medical Conditions: Underlying health issues, including thyroid disorders and autoimmune diseases, elevate the risk of hair loss. Managing and treating these conditions can be key in preventing or mitigating the impact on hair health.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Poor nutrition, certain medications, and aggressive styling practices can contribute to hair loss. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, being mindful of medications, and practicing gentle hair care are essential steps in minimizing environmental risks.
The life cycle of your hair
The life cycle of your hair involves three main stages: anagen, catagen, and telogen. During the anagen phase, your hair actively grows, with cells dividing rapidly in the hair follicles. This phase can last for several years, determining the length of your hair. The catagen phase follows, marking a transitional period where hair growth slows down, and the follicle shrinks.
Finally, in the telogen phase, your hair rests before eventually shedding and making way for new hair to grow. Understanding this cycle is crucial for maintaining healthy hair, as factors like nutrition and stress can influence each stage, impacting overall hair quality. During the anagen phase, your hair actively grows, with cells dividing rapidly at the hair follicle.
Androgenetic alopecia
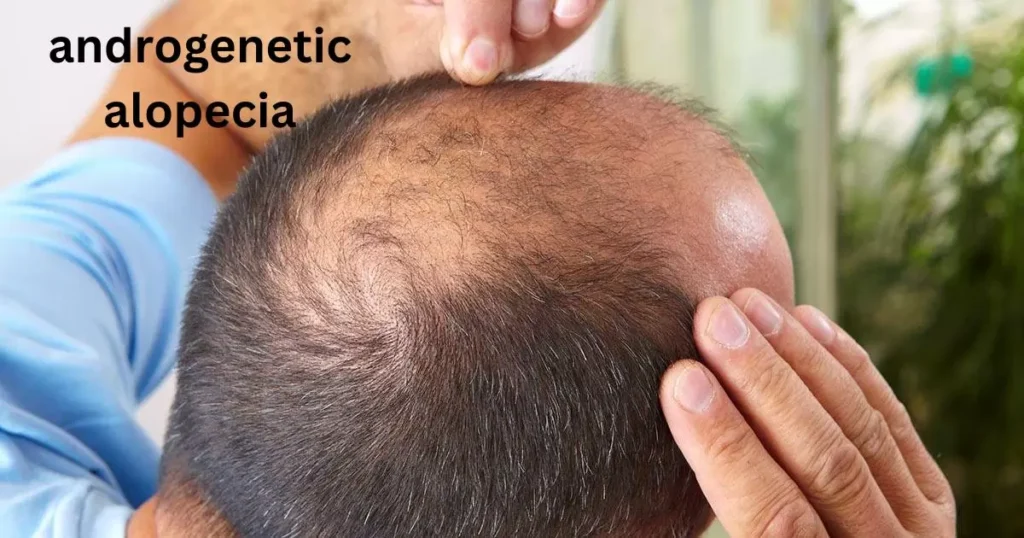
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male-pattern baldness, is a genetic condition characterized by the progressive thinning of hair in specific areas, typically at the crown and temples in both men and women. This condition is influenced by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, with androgens playing a significant role.
Androgens are male hormones that can cause hair follicles to shrink, leading to shorter and finer hair growth. While there is no cure for androgenetic alopecia, various treatments, such as medications and hair transplant surgery, aim to slow down hair loss or promote regrowth, providing options for managing this common form of hair thinning.
The main reason for hair fall
The primary cause of hair fall is multifaceted and can stem from various factors. One major contributor is genetics, as hereditary factors play a crucial role in determining hair health. Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can also lead to hair loss.
Poor nutrition, deficiency in essential vitamins and minerals, and an unhealthy lifestyle can contribute to weakened hair follicles. Stress and certain medical conditions may further exacerbate the issue. Understanding and addressing these underlying causes, along with adopting a balanced diet and lifestyle, are essential steps toward preventing and managing hair fall.
FAQs
What causes female hair loss?
Female hair loss can result from factors like hormonal changes, genetics, or medical conditions.
Is stress a factor in female hair loss?
Yes, high-stress levels can contribute to hair loss in women, impacting the hair growth cycle.
Can diet affect female hair loss?
Inadequate nutrition or extreme diets may lead to hair thinning and loss in females.
Are there specific medical conditions linked to hair loss in women?
Yes, conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can contribute to hair loss.
How can female hair loss be treated?
Treatment options may include medications, lifestyle changes, or medical procedures depending on the underlying cause of hair loss.
Conclusion
Female hair loss can stem from various factors. Hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause, may contribute to shedding. Medical conditions like thyroid disorders and polycystic ovary syndrome can also play a role. Nutritional deficiencies, stress, and certain medications may impact hair health.
Genetics and aging are additional factors influencing female hair loss. Understanding these diverse causes is crucial for effective management and seeking appropriate medical advice. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, addressing underlying health issues, and consulting with healthcare professionals can help mitigate and manage female hair loss effectively.


I like
Ap kia karty ha
Pingback: what helps women's hair loss?